Delegated Access
Delegated Access allows lower-privileged users to run specific scripts with elevated permissions by impersonating a power user. This provides controlled privilege escalation for trusted operations without granting users permanent elevated access.
Overview
Delegated Access solves a common problem: You want to give content authors access to specific administrative tasks without making them full administrators.
Without Delegated Access:
Grant users broad administrative roles
Risk: Users have more permissions than needed
Violates principle of least privilege
With Delegated Access:
Users keep limited permissions
Specific scripts run with elevated permissions
All actions are logged with both user identities
This feature was introduced in SPE with #1283
Use Cases
Content Author Needs Publishing Rights
Scenario: Content authors need to publish items but shouldn't have global publish rights.
Solution: Create a script that publishes specific items, configured to run as an administrator via delegated access.
Reports Requiring Administrative Access
Scenario: Managers need to run reports that query all items, but they have limited content access.
Solution: Configure the report script to impersonate an administrator, allowing full content access for the report only.
Bulk Operations on Protected Content
Scenario: A user needs to perform bulk updates on items they normally can't modify.
Solution: Create a controlled script with delegated access that performs the specific operation.
Workflow Actions
Scenario: Users need to trigger workflow commands that require elevated permissions.
Solution: Workflow scripts run with delegated access to perform administrative actions.
How It Works
Components
Delegated Access Item - Configuration item that defines the delegation
Requester Role - Sitecore role containing lower-privileged users
Impersonated User - Power user account whose permissions are used
Delegated Scripts - Specific scripts that run with elevated permissions
Execution Flow
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Create Delegated Access Item
Navigate in Content Editor to where delegated access configurations are stored and use the insert option.
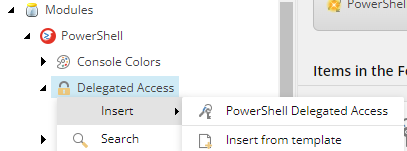
Step 2: Configure Requester Role
Enter the role that contains the lower-privileged users who should have delegated access.
Field: Requester Role
Example Values:
sitecore\Elevated Unlock- Custom role for editors
Why use roles instead of users?
Easier to manage
Follows role-based access control (RBAC) best practices
Changes apply to all role members automatically
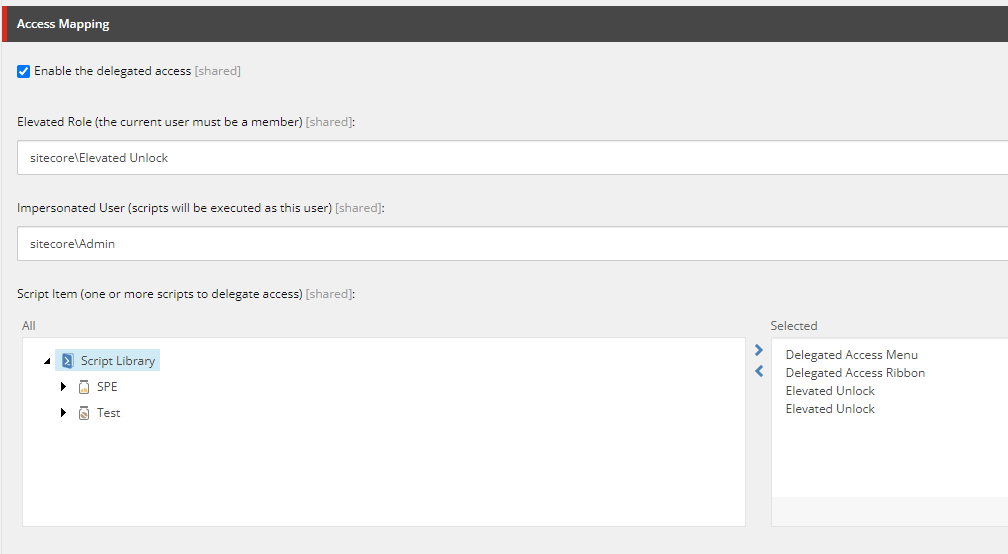
Step 3: Configure Impersonated User
Enter the user account whose permissions will be used when scripts execute.
Field: Impersonated User
Example Values:
sitecore\Admin- Full administrative accesssitecore\PowerUser- Custom account with specific elevated permissions
Security Consideration: The impersonated user should have the minimum permissions needed for the delegated scripts. Don't always use sitecore\Admin - create dedicated service accounts with specific permissions instead.
Step 4: Select Delegated Scripts
Choose which scripts and libraries should run with delegated access and ensure the appropriate rules are configured.
See the Security Management script module for more examples:
/sitecore/system/Modules/PowerShell/Script Library/SPE/Tools/Security Management
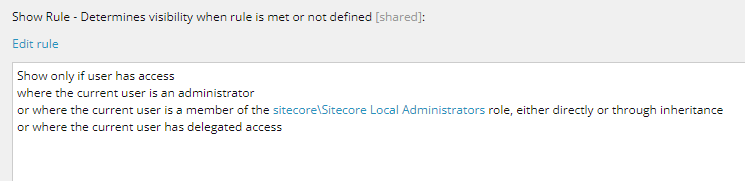
What to include:
Scripts that should run with elevated permissions
Script libraries containing those scripts
Scripts with rules that check for delegated access
Multilist Field: Select from available PowerShell scripts and script libraries.
Step 5: Enable the Configuration
Check the "Enabled" field to activate the delegated access configuration.
Field: Enabled (checkbox)
Important: Test thoroughly before enabling in production. Delegated access grants powerful permissions to lower-privileged users.
Audit Logging
All delegated access operations are logged to the SPE log file.
Log Entry Format:
Log Components:
Timestamp: When the script executed
Script ID: Unique identifier for the script
Context User: The actual logged-in user
Impersonated User: The elevated account used for execution
Monitoring Delegated Access
Regular log review should include:
✅ Monitor for:
Unexpected impersonation attempts
Scripts running as admin that shouldn't
Failed delegated access attempts
Unusual patterns (same user repeatedly, odd times)
Example log analysis query:
Best Practices
Security Recommendations
✅ Do:
Use dedicated service accounts instead of
sitecore\Adminwhen possibleLimit delegated scripts to specific, necessary operations
Regularly audit who has delegated access (review role membership)
Monitor SPE logs for delegated access usage
Test delegated access configurations in non-production first
Document why each delegated access configuration exists
Use confirmation dialogs in delegated scripts for destructive operations
Implement input validation in all delegated scripts
Set appropriate item-level security on delegated access items
❌ Don't:
Grant delegated access to broad roles like "Everyone"
Always impersonate
sitecore\Admin- use least privilegeAllow arbitrary code execution in delegated scripts
Forget to enable logging in delegated scripts
Skip user confirmations for destructive operations
Create delegated access "just in case" - only when needed
Allow users to modify delegated access configurations
Delegate scripts that can modify security or create users
Configuration Guidelines
Impersonated User
Dedicated service account
Easier to audit, limited permissions
Requester Role
Specific, narrow role
Limits who can use delegation
Script Scope
Single, focused operation
Reduces risk of abuse
Logging
Always log delegated actions
Audit trail for compliance
Testing
Test in QA first
Catch security issues before production
Review
Quarterly access review
Remove unused delegations
Script Security
When writing scripts for delegated access:
Validate All Input:
Limit Scope:
Confirm Destructive Operations:
Log Actions:
Troubleshooting
Delegated access doesn't work
Possible causes:
Delegated access item is not enabled
User is not in the requester role
Script is not selected in the delegated scripts field
Script library containing the script is not selected or enabled.
Solution: Verify all configuration fields and ensure the user is in the correct role.
Script runs with current user permissions instead of impersonated
Cause: Script or script library not included in delegated scripts selection.
Solution: Add both the script AND its parent library to the delegated scripts field.
Can't see delegated access insert option
Cause: Insert options not configured or user lacks permissions.
Solution: Verify insert options are configured on the parent item and user has write access.
Impersonated user doesn't have expected permissions
Cause: Impersonated user account lacks necessary Sitecore permissions.
Solution: Grant the impersonated user account the required Sitecore roles and item permissions.
Security Considerations
Risks
Privilege Escalation Abuse
Limit scripts to specific operations, validate input
Over-Privileged Impersonation
Use dedicated accounts with minimal required permissions
Broad Role Assignment
Only grant delegated access to specific, trusted roles
Script Modification
Protect script items with item-level security
Logging Gaps
Ensure all delegated operations are logged
Defense in Depth
Layer multiple security controls:
Role Membership - Only trusted users in requester role
Script Security - Item-level security on delegated scripts
Input Validation - Scripts validate and limit operations
Confirmations - User must confirm destructive actions
Logging - All operations logged
Auditing - Regular log review
Least Privilege - Impersonated users have minimum permissions
Related Topics
Security Policies - Understand SPE security model
Session Elevation - Additional authentication layer
User and Role Management - Managing Sitecore roles
Logging and Monitoring - Audit delegated access usage
References
GitHub Issue #1283 - Feature introduction
Last updated